Postgres Logical Replication and CDC - 1
Postgres 作为目前最流行的数据库之一,自身也在不断的发展。从 Postgres 10 开始,它内置了逻辑复制功能。逻辑复制不仅可以实现更灵活的数据备份,也可以作为 CDC (Change Data Capture) 架构的基础。
As one of the most popular databases, Postgres itself is constantly evolving. Starting from Postgres 10, it has built-in logical replication. Logical replication can not only achieve more flexible data backup, but also serve as the basis of the CDC (Change Data Capture) architecture.
历史
Postgres 对逻辑复制的支持经历了好几年的开发,主要由一家叫 2ndQuadrant 的公司开发并且提交到 Postgres 的。
Postgres’ support for logical replication has gone through several years of development, I think it mainly developed by a company called 2ndQuadrant and submitted to Postgres.
关于 2ndQuadrant 的历史,请参考: https://en.everybodywiki.com/2ndQuadrant。2ndQuadrant 在 2020 年 9 月被 EDB 公司收购: https://www.2ndquadrant.com/en/blog/how-edb-became-the-leader-in-the-postgres-market/。 For the history of 2ndQuadrant, please refer to: https://en.everybodywiki.com/2ndQuadrant. 2ndQuadrant was acquired by EDB in September 2020: https://www.2ndquadrant.com/en/blog/how-edb-became-the-leader-in-the-postgres-market/.
逻辑复制相关的功能主要是 2ndQuadrant 公司在开发自己的 Postgres-BDR 产品时设计并开发的。BDR 是一个 Postgres 集群解决方案,在这个产品开发过程中,2ndQuadrant 产生了对逻辑复制的需求,那是在 Postgres 9.2 版本之前。这篇文章记录了 BDR 的开发历史, https://www.2ndquadrant.com/en/blog/bdr-history-and-future/。逻辑复制的相关支持是慢慢提交到 Postgres 内核中的,从 9.2 版本增加对 trigger 的支持开始,9.4 版本支持 logical decoding,9.6 版本完成了所有的 logical decoding 必要 feature 的支持,10 版本开始支持 logical replication。整个过程是很漫长的。下图是 2ndQuadrant 提供的,描述了逻辑复制相关功能在 Postgres 上的演进。
The functions related to logical replication are mainly designed and developed by 2ndQuadrant when developing its own Postgres-BDR product. BDR is a Postgres cluster solution. During this product development process, 2ndQuadrant generated a need for logical replication, which was before Postgres 9.2. This article records the development history of BDR, https://www.2ndquadrant.com/en/blog/bdr-history-and-future/. The support for logical replication is slowly submitted to the Postgres kernel. Starting with the addition of trigger support in version 9.2, version 9.4 supports logical decoding, version 9.6 completes the support for all necessary features of logical decoding, and version 10 starts to support logical replication . The whole process is very long. The following figure is provided by 2ndQuadrant and describes the evolution of logical replication related functions on Postgres.
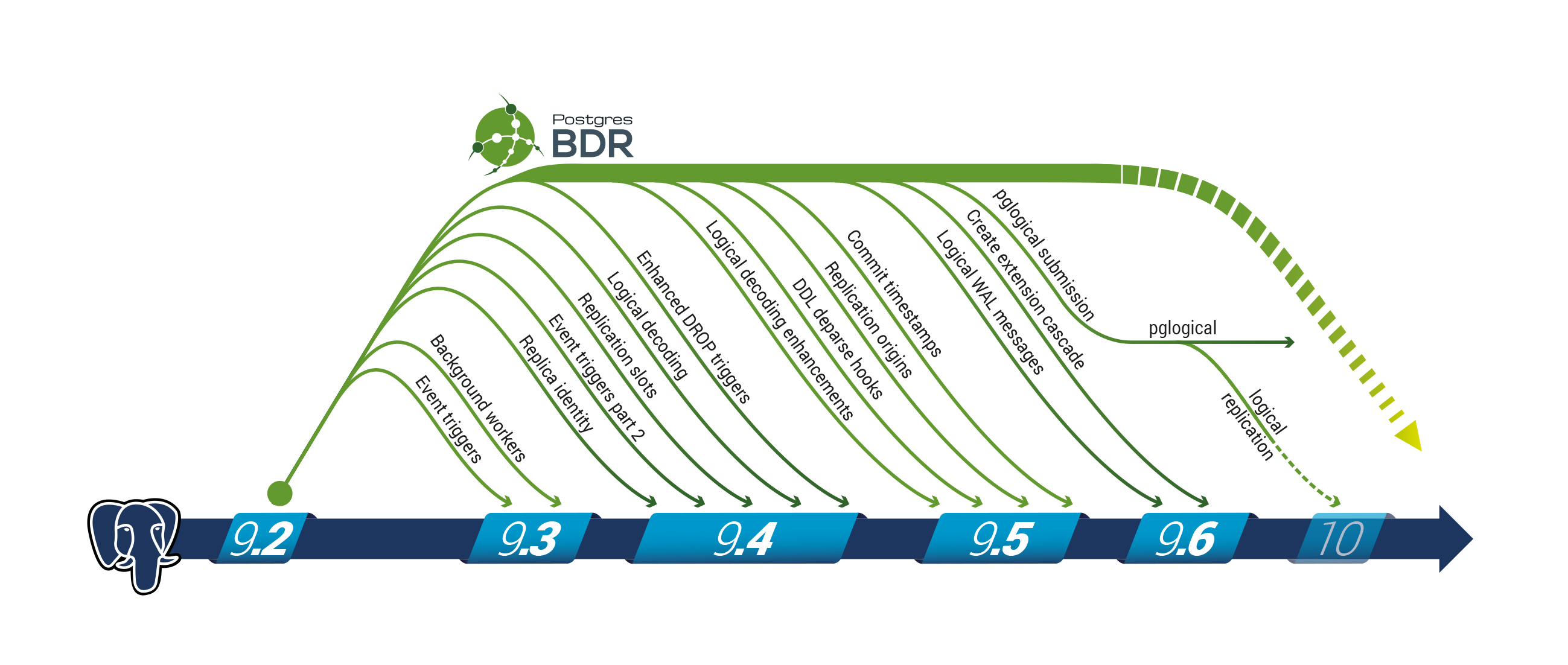
Picture from: https://www.2ndquadrant.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/infograph-bdr-1.png
9.6 版本算是一个经典版本。在 9.6 版本发布了之后,BDR 可以在 Postgres 不打补丁的情况下就提供支持 (之前 9.4 版本需要打一个大 patch,https://www.2ndquadrant.com/en/blog/bdr-is-coming-to-postgresql-9-6/)。
The 9.6 version is considered a classic version. After the release of version 9.6, BDR can support Postgres without patching (previous version 9.4 requires a large patch, https://www.2ndquadrant.com/en/blog/bdr-is-coming- to-postgresql-9-6/).
此外,还有个扩展,叫做 pglogical。它是从 BDR 项目中剥离出来的,从 9.4 版本开始支持逻辑复制功能。虽然从 Postgres 10 版本开始,已经内置了逻辑复制,但是 pglogical 依旧继续在开发之中,主要的原因是 pglogical 作为一个扩展,可以更快的进行 feature 开发和升级。在这篇文章中,解释了为什么要把逻辑复制功能引入到 Postgres 中,以及为什么引入之后还继续开发 pglogical: https://www.2ndquadrant.com/en/blog/pglogical-logical-replication-postgresql-10/。
In addition, there is an extension called pglogical. It is stripped from the BDR project and supports the logical replication function since version 9.4. Although the logical replication has been built-in since Postgres 10, pglogical is still under development. The main reason is that pglogical, as an extension, can develop and upgrade features faster. This article explained why the logical replication function was introduced into Postgres, and why the development of pglogical was continued after the introduction: https://www.2ndquadrant.com/en/blog/pglogical-logical-replication-postgresql- 10/.
可以这么认为:
- Postgres 9.4 ~ 9.6 版本,主要是引入了 logical decoding 功能,作为逻辑复制基础。
- Postgres 10 版本引入的逻辑复制功能,也就是把 pglogical 的核心功能集成到 Postgres 里。
Think of it this way:
- Postgres 9.4 ~ 9.6 version, mainly introduces the logical decoding function, as the basis of logical replication.
- The logical replication function introduced in Postgres 10 version is to integrate the core function of pglogical into Postgres.
Logical Decoding
Logical decoding 是 Postgres 9.4 引入的,通过看 9.4 版本的文档 https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.4/logicaldecoding.html,可以知道,从 9.4 版本开始 logical decoding 的功能就已经比较完善了。
Logical decoding Postgres 9.4 is introduced, by the 9.4 version of the document https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.4/logicaldecoding.html, you can see that at version 9.4, logical decoding was almost fully functional.
Logical decoding 的功能主要在 Postgres 内部提供了一种将数据库中的数据上所发生的改变的事件导出的手段。官方文档的原文是:
The function of logical decoding mainly provides a means to export the events of changes in the data inside Postgres. The original text of the official document is:
PostgreSQL provides infrastructure to stream the modifications performed via SQL to external consumers.
实现原理
它的根本原理是在数据库内部将 WAL 文件的内容按照一定的格式输出,事件输出的顺序等同于 WAL 的写入顺序(如果一个事件可以输出的话,否则该事件就会直接被忽略)。对于 Postgres 来说,实现 logical decoding 就是在 WAL flush 到磁盘之后,调用 replication slot 的指定的 plugin 的回调函数。官方文档解释了每个回调函数的作用: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/logicaldecoding-output-plugin.html。在本文撰写的时候,Postgres 的最新版本是 13,14 版本正在开发中。从最新的代码中可以看到,在 14 版本中,Postgres 会开始支持未提交事务的逻辑复,所以 plugin 回调结构体 struct OutputPluginCallbacks 中增加了很多以 stream_ 开头的回调函数。
Its fundamental principle is to output the contents of the WAL file in a certain format within the database, and the sequence of event output is equivalent to the writing sequence of WAL (if an event can be output, otherwise the event will be ignored). For Postgres, implementing logical decoding is to call the callback functions of the specified plugin of the replication slot after the WAL flush to the disk. The official document explains the role of each callback function: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/logicaldecoding-output-plugin.html. At the time of this writing, the latest version of Postgres is 13, and version 14 is under development. You can see from the latest code in version 14, Postgres will begin to support complex logic uncommitted transactions, so the plugin callback structure struct OutputPluginCallbacks adds a lot of callback functions with the prefix stream_.
Logical decoding 中有一个 logical replication slot ( 简称 replication slot) 的概念。一个 replication slot 代表了一个事件输出流,用于将 WAL 记录的事件发送给订阅者。replication slot 主要功能有两个:
- 使用预先配置好的 output plugin 将 WAL 内容转换成输出格式。
- 维护需要使用的 WAL 位置,包括订阅者开始消费的位置,以及订阅者已经 flush 的位置(可以把订阅者当成一个备库,当备库向主库报告自己已经将某个位置之前的 WAL 都持久化之后,主库就可以将该位置之前的 WAL 文件回收了)。
There is a concept of logical replication slot (referred to as replication slot) in logical decoding. A replication slot represents an event output stream, used to send WAL recorded events to subscribers. There are two main functions of replication slot:
- Use the pre-configured output plugin to convert WAL content into output format.
- Maintain the WAL location that needs to be used, including the location where the subscriber starts to consume, and the location where the subscriber has been flushed (you can treat the subscriber as a standby database, when the standby database reports to the main database that it has persisted the WAL before a certain location, the main dastabase can reclaim the WAL file before the location).
data=# select * from pg_replication_slots ;
slot_name | plugin | slot_type | datoid | database | temporary | active | active_pid | xmin | catalog_xmin | restart_lsn | confirmed_flush_lsn | wal_status | safe_wal_size
--------------+----------+-----------+--------+----------+-----------+--------+------------+------+--------------+-------------+---------------------+------------+---------------
myslot | pgoutput | logical | 16384 | data | f | f | | | 622 | 0/1765268 | 0/1765282 | reserved |
(1 row)
这里比较难理解的是 restart_lsn 和 confirmed_flush_lsn 这两个列的值。
Here it is difficult to understand restart_lsn and confirmed_flush_lsn.
confirmed_flush_lsn 表示 consumer 已经收到并且回复确认的 WAL 的 LSN。早于该值的 WAL 无法再被 consumer 获取。这个值在 consumer 每次通过 StandyStatusUpdate 消息更新时都会被修改。
confirmed_flush_lsn means the address (LSN) up to which the logical slot’s consumer has confirmed receiving data. Data older than this is not available anymore. This value updated by each consumer’s StandyStatusUpdate message.
官方文档对于 restart_lsn 的描述就没有这么清晰了:
Official document for restart_lsn is not so clear:
The address (LSN) of oldest WAL which still might be required by the consumer of this slot and thus won’t be automatically removed during checkpoints unless this LSN gets behind more than max_slot_wal_keep_size from the current LSN. NULL if the LSN of this slot has never been reserved.
我在邮件列表里找到了几个相关的讨论,可能最有用的两个如下:
I found some discussion about restart_lsn, the following two might be useful:
In general, the restart_lsn and confirmed_flush_lsn are advanced in different ways so you might see some difference but it should not be this much. The confirmed_flush_lsn is updated when we get confirmation from the downstream node about the flush_lsn but restart_lsn is only incremented based on the LSN required by the oldest in-progress transaction.
By Amit Kapila
To make sure, replication delay or lag here is current_wal_lsn() - confirmed_flush_lsn. restart_lsn has nothing to do with replication lag. It is the minimum LSN the server thinks it needs for restarting replication on the slot.
How long have you observed the increase of the gap? If no long-transactions are running, restart_lsn is the current LSN about from 15 to 30 seconds ago. That is, the gap between restart_lsn and confirmed_flush_lsn would be at most the amount of WAL emitted in the last 30 seconds. In this case, that is estimated to be 235MB*30 = about 7GB or 440 in 16MB-segments even if the system is perfectly working. Anyway the publisher server would need to preserve WAL files up to about 68GB (in the case where checkpoint_timeout is 5 minutes) so requirement of 7GB by restart_lsn doesn’t matter.
By Kyotaro Horiguchi
从这两个逻辑复制的开发者的回复可以看出,restart_lsn 的作用不是用来表示下游节点的复制延迟大小的,只是用来指导 master 何时可以删除 WAL 文件。主要的原因是 logical decoding 和 checkpoint 进程都涉及到何时删除 WAL 文件,因此系统需要考虑多个值来确认哪些 WAL 文件是可以回收的。 (我在写这篇文章的时候,并没有阅读过 Postgres 的代码,所以我以上的结论是不准确的,也有可能是错误的。)
From the threads of the these two developers of logical replications, restart_lsn is not used to indicate replication delay, but to guide the main database when WAL files can be deleted. The main reason is that both logical decoding and checkpoint process involveed with WAL files deletion, so the system needs to consider multiple values to confirm which WAL files can be recycled. (When I was writing this article, I had not read the Postgres code, so my above conclusions are inaccurate and may be wrong. )
Output Plugin
Output plugin 是 logical decoding 里面决定输出格式的程序。这个 wiki 页面介绍了大部分的插: https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Logical_Decoding_Plugins. 本章介绍几个主要的插件。
Output plugin is the program that determines the output format in logical decoding. This wiki page introduces most of the plugins: https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Logical_Decoding_Plugins. This chapter introduces several major plugins.
test_decoding
在 9.4 版本里,只有一个内置的 test_decoding 的插件 (*https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.4/test-decoding.html*),它用于支持
In version 9.4, there is only one built-in plugin named test_decoding (* https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.4/test-decoding.html* ), which is used to support
SELECT * FROM pg_logical_slot_get_changes('test_slot', NULL, NULL, 'include-xids', '0');
这个插件的主要作用是提供一个简单的调试手段,同时作为其他插件开发的模板,并不适用于实现逻辑复制这样复杂的场景。这个插件的代码在: https://github.com/postgres/postgres/blob/master/contrib/test_decoding/test_decoding.c.
The main function of this plug-in is to provide a simple debugging method, and at the same time as a template for other plug-in development, it is not suitable for complex scenarios such as logical replication. The code for this plugin is at: https://github.com/postgres/postgres/blob/master/contrib/test_decoding/test_decoding.c.
pglogical
由于 test_decoding 只是提供了一个实现参考,所以在还没有 pgoutput 插件的时候,pglogical 程序自己实现了一个 plugin (https://github.com/2ndQuadrant/pglogical/blob/REL2_x_STABLE/pglogical_output.c) 。
Since test_decoding only provides an implementation reference, the pglogical program implements a plugin (https://github.com/2ndQuadrant/pglogical/blob/REL2_x_STABLE/pglogical_output.c) when there is no pgoutput plugin .
wal2json
https://github.com/eulerto/wal2json 这个插件是一个比较流行的插件,因为它的输出是 JSON 格式的,相当容易理解以及用程序解析。不过这个插件不是 Postgres 内置的,需要自己安装。但是由于其非常简单易用,有些云服务会在自己的 Postgres 服务中内置这个这个插件,例如 Azure (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/postgresql/concepts-logical).
https://github.com/eulerto/wal2json This plug-in is a popular plugin because its output is in JSON format, which is quite easy to understand and parse with programs. But this plugin is not built-in Postgres, you need to install it yourself. But because it is very simple and easy to use, some cloud services will install this plugin in their Postgres service, such as Azure ( https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/postgresql/concepts-logical ).
pgoutput
在 Postgres 10 里,内置了一个 pgoutput 插件,为逻辑复制功能提供基础。pgoutput 实现了一个二进制协议,而且会在多个 Postgres 版本之间保持稳定(这样才能实现跨版本的逻辑复制)。这个协议属于 Postgres 后端协议的一部分,具体的协议定义见: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/protocol-logicalrep-message-formats.html。相比与 wal2json 这种文本格式的插件,pgoutput 插件的二进制协议的优点是性能好,缺点是较难解析。该插件的代码在: https://github.com/postgres/postgres/blob/master/src/backend/replication/pgoutput/pgoutput.c.
In Postgres 10, a pgoutput plug-in is built in to provide a basis for logical replication. pgoutput implements a binary protocol and will remain stable across multiple Postgres versions (so that it can achieve cross-version logical replication). This protocol is part of the Postgres backend protocol. For specific protocol definitions, please see: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/protocol-logicalrep-message-formats.html. Compared with the text format plug-in of wal2json, the binary protocol of the pgoutput plug-in has the advantage of good performance, but the disadvantage is that it is difficult to parse. The code of the plugin is at: https://github.com/postgres/postgres/blob/master/src/backend/replication/pgoutput/pgoutput.c.
如果使用 Golang 进行开发,我已经在 github.com/jackc/pglogrepl 这个库中增加了对 pgoutput 的支持 (https://github.com/jackc/pglogrepl/pull/14)。你可以直接利用这个库中的 example 代码作为自己开发 subscriber 的基础: https://github.com/jackc/pglogrepl/tree/master/example/pglogrepl_demo。
If you use Golang development, I have adds support for the protocol in Github repo: github.com/jackc/pglogrepl (support for pgoutput of https://github.com/jackc/pglogrepl/pull/14 ). You can directly use the example code in this repo as the basis for your own development of subscribers: https://github.com/jackc/pglogrepl/tree/master/example/pglogrepl_demo.
Update
- Translate From Chinese to English with Google translate, then checking and editing.
 本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。
本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。